PATENTED TECHNOLOGY
Aurum stands out for its patented technology that ensures a 100% plant-based product with high qualities and qualities. Their focus is based on using the most advanced technology in the production process of plant-based products. This innovative technology allows for the production of high-purity plant proteins, free from impurities, and with an excellent nutritional profile.
Aurum’s technology distinguishes itself with its efficiency in the extraction and purification of plant proteins, ensuring a superior quality end product. Moreover, this patented technology is also characterized by its sustainable approach, minimizing environmental impact and maximizing the utilization of plant resources.
With its advanced technology, Aurum leads the way in plant protein production, offering high-quality, nutritionally valuable solutions for the food industry, nutritional supplements, and animal nutrition.
ACCELERATED HYDRATION AND PROCESSING OF PLANT-BASED PRODUCTS FROM LEGUMES, CEREALS, AND SEEDS
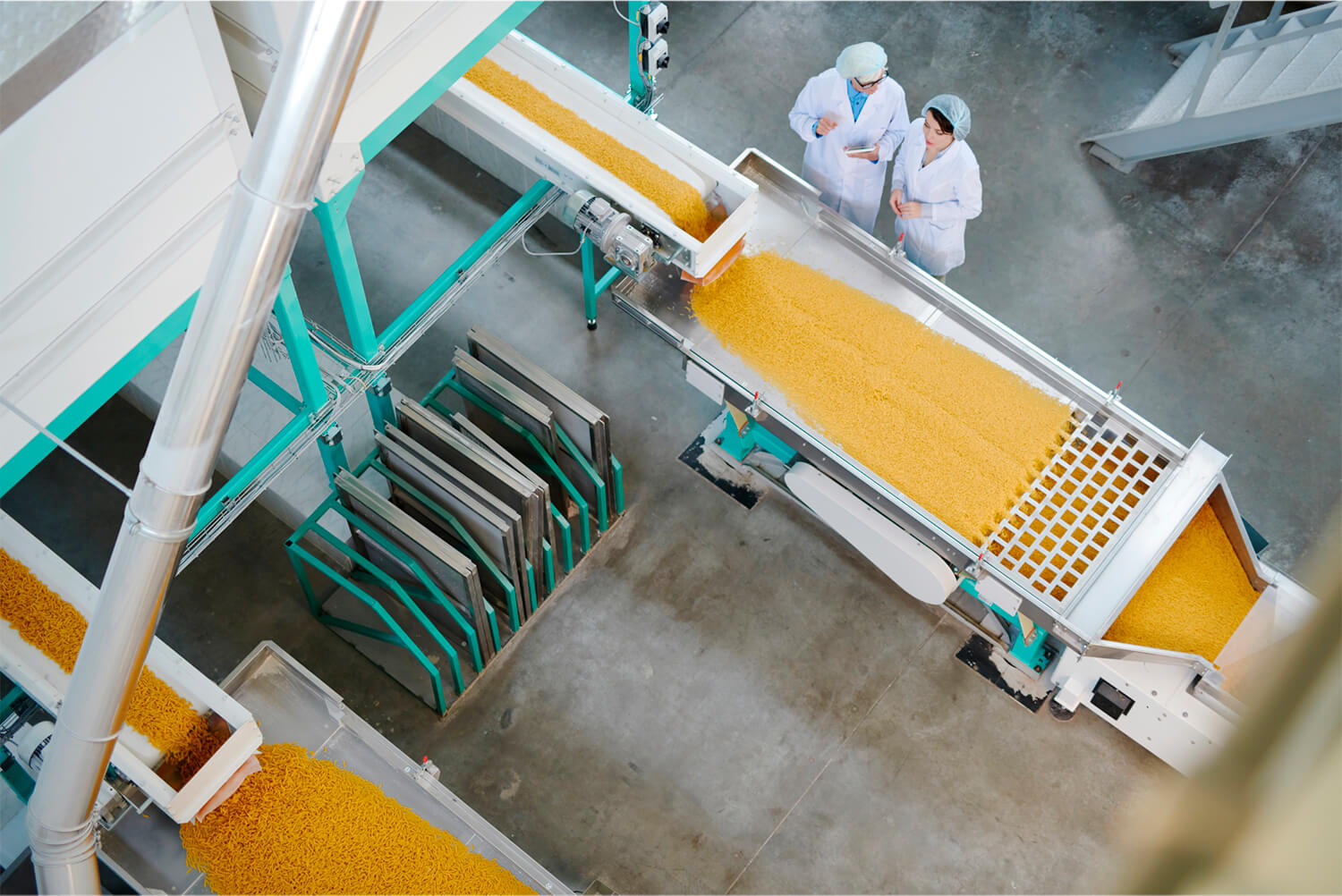
Our Accelerated Hydration system is an innovative technology that enables quick and efficient hydration of ingredients, improving the production process and ensuring the quality of the final products.
On the other hand, processing legumes, cereals, and seeds allows for the production of various products, ranging from wet and dehydrated fibers to plant-based beverages and protein powder, which have a wide range of applications in the food and nutritional industries.
ACCELERATED HYDRATION
We have been developing accelerated hydration technology with patented processes for many years, achieving 100% effective results. Thanks to our pilot plant, we can perfectly replicate the temperature-time profiles of the product and the specific water tailored to each customer, so you can see in advance the result of what you will obtain.
Hydration times are reduced to just 45 and 90 minutes, depending on the type of vegetable, and these times can be regulated by our specific software. Customer satisfaction is our success.
Our system consists of a continuous input of product/material into a tank with an internal rotation system developed by AURUM, which prevents clumping while ensuring effective hydration.
The temperature profile changes along the column, allowing the legumes to start hydrating with cooler water at the beginning and reaching a point at the end of hydration where they can even be partially precooked or blanched within the same column.
The hydration time, which can range from 45 to 90 minutes depending on the type of legume or raw material, is adjustable through programming.
Similarly, we can adapt the plant configuration to:
– One hydration column and one continuous cooking column.
– Three hydration tanks for continuous production and batch processing in each tank.
– Specially designed with horizontal tanks for installations under 3 meters in height.
Our system is capable of handling capacities from 200 kg/hour of raw material input to 1.5 tons/hour of dry raw material input.


Chickpea Input raw
1000 kg
2000 kg
3000 kg
Chickpea output cooked/hydrated
2000 kg
3000 kg
6000 kg
HYDRATED WET FIBERS
The process of obtaining wet fibers includes wet extraction, followed by drying through hot air or freeze-drying. Dehydrated fibers are then ground and sieved to obtain fiber powder. These fibers have various key applications.
In the food industry, they are used as additives to improve the texture, stability, and nutritional quality of foods such as bread, cereals, soups, and meat products, increasing fiber content and enhancing digestive health.
In dietary supplements, they are employed in capsules, powders, or tablets to boost fiber intake and improve digestive health.
In the pharmaceutical industry, they are used as excipients in medications, enhancing their stability, bioavailability, and formulation.
In animal nutrition, they are included in pet foods, livestock feeds, and poultry feeds, providing necessary dietary fiber for animal health and proper digestion.
In the textile industry, they are processed and used as base materials for the production of yarns, fabrics, clothing, and upholstery.
PROTEIN POWDER
The production of plant-based protein powder involves several stages. First, proteins are extracted from the plant raw material using methods such as alkaline or acid extraction. Then, they are purified, and impurities are removed through techniques like precipitation and ultrafiltration. After obtaining concentrated and purified protein, it is dried to turn it into powder.
Plant-based protein powder has a wide range of uses and applications. In the food industry, it is used as an ingredient in vegan and vegetarian products, serving as an alternative to animal proteins. It is also added to shakes, energy bars, baked goods, and processed foods to increase their protein content. Additionally, it is used in nutritional and sports supplements because it provides a complete and high-quality protein source.
Plant-based protein powder also finds applications in the animal food industry, including pet food and livestock feed, as it offers a nutritious and sustainable option.
In summary, the production process of plant-based protein powder involves extraction, purification, and drying, and its uses span from vegan foods to nutritional supplements and animal nutrition.
PLANT-BASED BEVERAGES
The production of plant-based beverages involves several stages. First, plant-based ingredients such as oats, almonds, sunflower seeds, hemp, or chickpeas are selected and processed. Next, the nutritious components are extracted, typically through soaking, grinding, and filtration. Water is added to achieve the desired consistency, and other ingredients like natural sweeteners or flavors can be added to enhance taste.
Plant-based beverages are a popular alternative to dairy and are consumed by vegans, lactose intolerant individuals, or those interested in healthier options. These beverages are used as milk substitutes in coffee, tea, smoothies, cereals, and cooking recipes. Furthermore, they serve as a base for making ice creams, yogurts, and baked goods.
Oat, almond, sunflower, hemp, and chickpea-based beverages offer different nutritional profiles and flavors, making them versatile and appealing to various dietary preferences. The production process aims to preserve nutrients and provide a sustainable and natural option for those seeking plant-based alternatives in their diet.
Extraction and processing of starches and plant fibers
Starch is a valuable source of carbohydrates found abundantly in various plants such as corn, potatoes, wheat, and rice. The process of starch extraction and processing typically involves the following steps:
Starch-rich plant ingredients are ground into a paste or pulp.
The pulp is washed with water to remove other impurities and soluble components.
Through filtration or centrifugation processes, the starch is separated from other components such as proteins and fibers.
The starch is dried to obtain a fine and stable powder.
In the food industry, starch is used as a thickener and stabilizer in soups, sauces, creams, desserts, and ice creams. It is also used in the production of bread, cookies, pasta, and bakery products to provide structure and texture.
In the beverage industry, starch is used in beer production and in the clarification of juices.
Examples of end products based on starch include:
Tomato Sauce: Corn starch is used to thicken tomato sauce and give it a smoother and more homogeneous texture.
Sandwich Bread: Wheat starch is used in the production of sandwich bread to give it its characteristic structure and texture.
Yogurt: Some yogurt varieties may contain starch as a thickener to achieve a creamier consistency.
Extraction and processing of fibers:
Dietary fibers primarily come from fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
Extraction and processing of fibers
Vegetable sources are processed to extract dietary fibers and remove other components.
The extracted fibers are washed and purified to remove impurities and residues.
The fibers are dried to obtain a stable product.
In the food industry, fibers are used as additives to improve texture, increase fiber content, and promote digestive health in food products.
Examples of end products with fibers include:
Granola Bars: Dietary fibers are added to granola bars to enhance their nutritional content and promote digestive health.
Whole Grains: Whole grains contain dietary fibers that facilitate digestion and promote a feeling of fullness.
Whole Wheat Bread: Whole wheat bread contains more fiber than white bread, making it a healthier and digestion-friendly option.
In conclusion, the extraction and processing of starches and plant fibers are essential processes in the food industry, utilized in a wide range of products to enhance texture, nutritional content, and digestive health.
FLEXIBILITY OF RAW MATERIALS
We have processing solutions for a wide range of crops. As new products are developed, there is increasing interest in new types of proteins with different characteristics in terms of taste, nutrition, and/or texture.
Adding the right protein can also improve technical functionalities, including the ability to stabilize multiphase systems like foams and emulsions. Furthermore, the composition and quality of proteins can vary daily. Therefore, our systems have been meticulously designed to ensure adaptability and maintain consistent performance.
Please feel free to contact us if you would like to explore the potential of using various raw materials and learn more about our flexible designs.





